Abstract
Acne vulgaris is a major problem despite a vast array of treatment available for acne. Rising antibiotic drug resistance consequent to the widespread use of topical antibiotics is causing concern and effective non-antibiotic treatments are needed. In this study, the efficacy and tolerability of novel lotion (Aknicare Lotion) containing triethyl citrate and ethyl linoleate in the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris is tested.
Results
Active treatment was shown to be statistically superior to non-active product in the total inflamed and non-inflamed acne lesions. The active lotion showed a rapid response with obvious reduction in lesion counts and acne grading by 4 weeks.
Controlling of sebum (oil)
- – Active lotion (Aknicare Lotion)
- – Non-active lotion (Placebo)
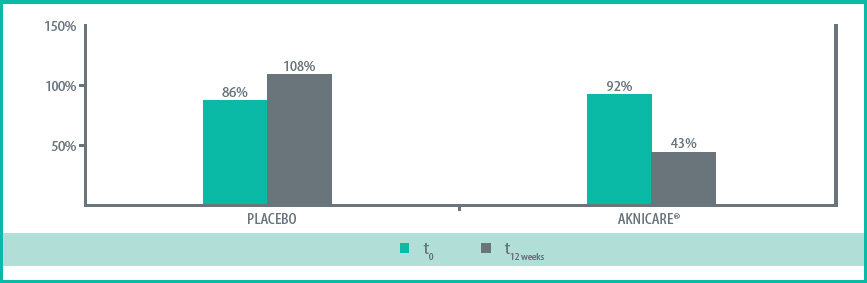
After 12 weeks of treatment, sebum excretion was reduced by up to 68%, at an average of 53%
Overall assessment to acne lesion and severity
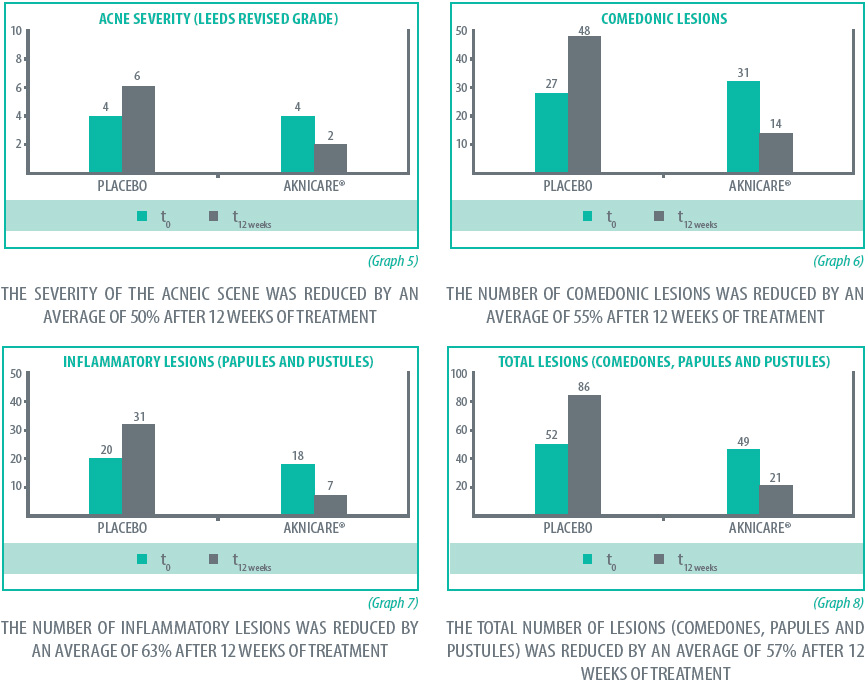
This study concludes the active lotion (Aknicare Lotion) is an effective and significant treatment for acne vulgaris.
Before and after treatment